Welcome to the world of investing, where decisions can have a huge impact on our financial future. One important concept that investors must understand is loss aversion and its impact on investment strategy. Loss aversion refers to our natural tendency to feel the pain of losses more acutely than the pleasure of gains, and it can significantly influence how we approach investment decisions.
When it comes to investing, we humans are wired in a peculiar way. We tend to be more sensitive to potential losses than to potential gains. This psychological phenomenon, known as loss aversion, has a profound effect on how we make investment decisions. It can lead us to take unnecessary risks or make irrational choices based on fear rather than logic.
Loss aversion not only affects individuals, but it also has a broader impact on investment strategy as a whole. Investors, fund managers, and financial institutions need to understand and account for loss aversion when formulating investment strategies. By acknowledging and addressing this cognitive bias, they can build more robust and effective investment approaches that can withstand the ups and downs of the market.
So, if you’re ready to dive into the fascinating world of loss aversion and its impact on investment strategy, let’s explore how this psychological bias influences our decision-making process and discover strategies that can help us navigate the complex world of investing with confidence. Get ready to challenge your thinking and gain valuable insights into how our minds can sometimes play tricks on us when it comes to our investments. Let’s get started!

Understanding Loss Aversion and Its Impact on Investment Strategy
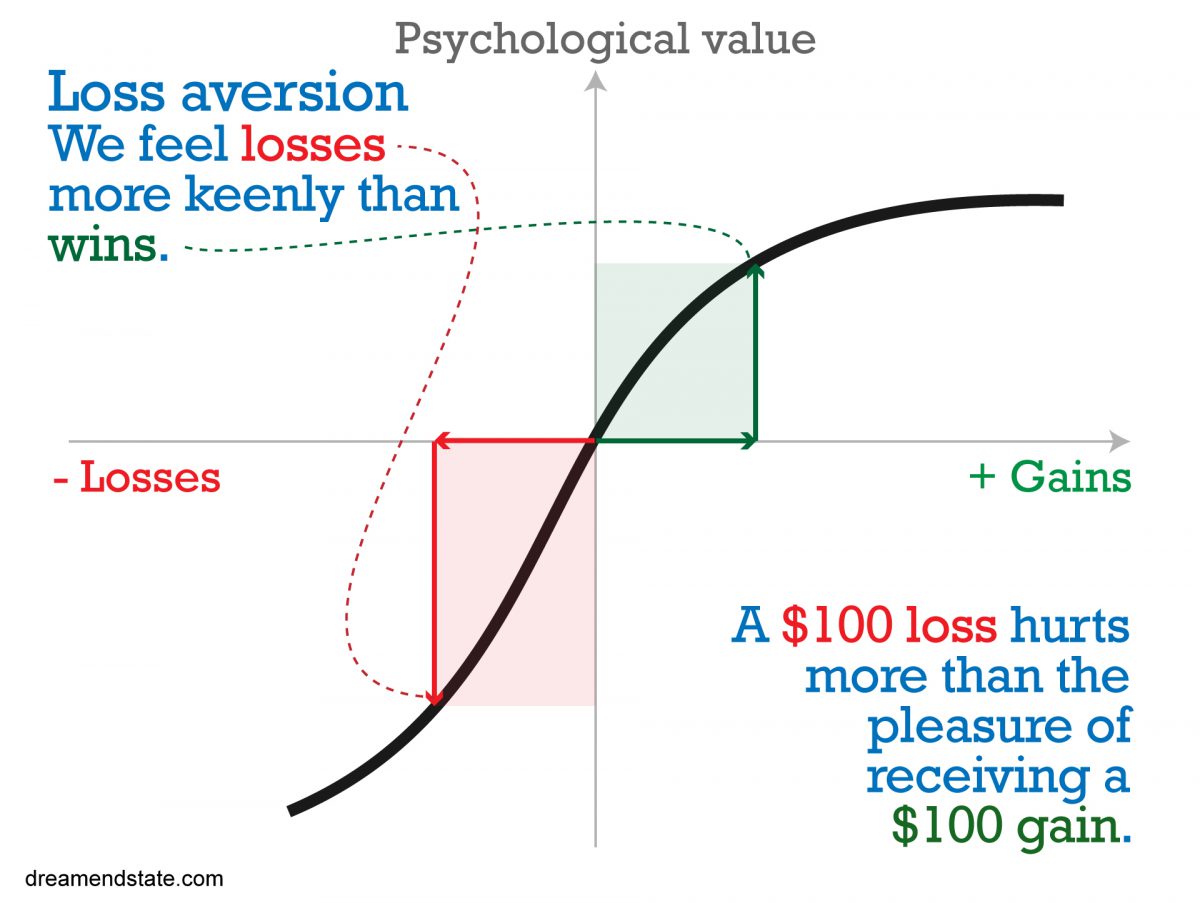
Loss aversion is a cognitive bias that affects our decision-making when it comes to financial investments. It refers to the tendency for humans to feel the pain of losses more strongly than the pleasure of gains. This psychological phenomenon has significant implications for our investment strategies and can influence how we approach risk and opportunity in the financial market.
Loss aversion is rooted in our fear of losing something we already possess. It causes us to become overly cautious and reluctant to take risks, even if the potential for gains is high. This bias can lead investors to make irrational decisions, such as holding onto losing investments for too long or selling winning investments too quickly.
The Impact of Loss Aversion on Investment Decision Making
Loss aversion can have a profound impact on our investment decision making. When we are faced with the possibility of losses, our risk tolerance decreases, and we become more focused on avoiding those losses rather than seeking gains. This bias can result in missed opportunities for significant returns.
For example, let’s say an investor buys a stock that starts to decline. Due to loss aversion, they may hesitate to sell the stock at a loss and hold onto it, hoping the price will rebound. This decision is driven by the fear of crystallizing the loss rather than a rational assessment of the stock’s future prospects. As a result, the investor may end up with a larger loss or miss out on other investment opportunities.
On the other hand, loss aversion can also lead investors to sell their winning investments too early. The fear of losing the gains already made can overshadow the potential for further appreciation. This premature selling can limit the investor’s overall returns and prevent them from fully realizing the value of their investments.
Strategies for Mitigating the Impact of Loss Aversion
While loss aversion is a natural human instinct, there are strategies investors can employ to mitigate its impact on their decision making. Understanding and managing this bias is crucial for achieving long-term investment success. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Diversify Your Portfolio:
Diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes and sectors can help reduce the impact of individual losses. When one investment performs poorly, the overall portfolio may still generate positive returns from other investments. This strategy can help alleviate the fear of losses and provide a more balanced approach to investing.
2. Set Clear Investment Goals:
Having clear investment goals and a well-defined investment plan can help counteract the emotional influence of loss aversion. By focusing on long-term objectives and adhering to a disciplined investment strategy, investors can avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market fluctuations.
3. Stay Informed and Seek Professional Advice:
Staying informed about market trends, economic indicators, and the performance of specific investments can help investors make more informed decisions. Additionally, seeking advice from financial professionals who can provide objective insights can provide a fresh perspective and help mitigate the impact of emotional biases.
The Role of Loss Aversion in Behavioral Finance Research
Behavioral finance is an area of study that explores the impact of human psychology and emotions on financial decision making. Loss aversion is one of the key concepts in this field, as it highlights how emotions can override rational thinking in investment strategies.
Loss Aversion and Prospect Theory
Prospect theory, developed by psychologists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky, further explains the role of loss aversion in decision making. According to prospect theory, individuals evaluate potential losses and gains relative to a reference point, usually their current status quo. Losses have a greater emotional impact than gains, leading to risk-averse behavior.
Prospect theory also introduces the concept of diminishing sensitivity, stating that as the magnitude of gains or losses increases, the emotional response diminishes. For example, the emotional impact of losing $1,000 is greater than the impact of gaining $1,000. This principle suggests that investors are more sensitive to small losses and less responsive to large gains, which can further reinforce loss aversion in investment decision making.
Loss Aversion and Market Volatility
Loss aversion can be particularly influential during periods of market volatility. When markets are experiencing significant fluctuations, the fear of losses intensifies, leading investors to make impulsive decisions driven by emotions rather than rational analysis.
During bear markets or periods of economic uncertainty, loss aversion can cause investors to panic and sell their investments at lower prices. This behavior can amplify the downward pressure on markets and create further volatility. Conversely, during bull markets, loss aversion can make investors hesitant to participate in the market’s upward momentum, potentially missing out on significant gains.
The Importance of Investor Education and Emotional Intelligence
Recognizing the impact of loss aversion on investment decisions is the first step towards managing its effects. Investor education programs that focus on behavioral finance can help individuals understand their biases and develop emotional intelligence in their investment approach.
By cultivating emotional intelligence, investors can learn to recognize and manage their emotional responses to market fluctuations. This self-awareness can help them make more rational and informed investment decisions, reducing the negative impact of loss aversion on their portfolios.
Investment strategies that take into account the influence of loss aversion and behavioral biases can lead to more balanced and successful investment outcomes. By understanding the psychological factors at play and adopting strategies to counteract them, investors can navigate the market with greater clarity and confidence.
Key Takeaways: Loss Aversion and Its Impact on Investment Strategy
- Loss aversion is the tendency for individuals to feel the pain of losses more strongly than the pleasure of gains.
- Loss aversion can impact investment strategy by causing investors to hold onto losing investments for longer than they should.
- Investors should be aware of their own biases and emotions when making investment decisions.
- Diversification and regular review of investments can help mitigate the impact of loss aversion on investment strategy.
- Understanding loss aversion can help investors make more rational and objective investment decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Loss aversion is a psychological phenomenon that affects our decision-making when it comes to investments. It refers to the tendency of individuals to feel the pain of a loss more strongly than the pleasure of a gain. This can lead to irrational behavior and impact our investment strategies. To help you better understand the concept of loss aversion and its impact on investment strategy, we have answered some common questions below.
1. How does loss aversion influence investment decisions?
Loss aversion can greatly influence investment decisions as it makes us more averse to taking risks. The fear of experiencing losses can often lead to avoiding investments altogether or seeking low-risk, low-return opportunities. This can hinder potential growth and limit the diversification of the investment portfolio. To overcome this bias, it is important to understand that taking calculated risks is a crucial part of investment strategy and that losses are a natural part of the investment journey.
By acknowledging and managing our loss aversion tendencies, we can ensure a more rational approach to investing that takes into account potential gains as well as losses. This may involve diversifying our portfolio, setting realistic expectations, and maintaining a long-term perspective.
2. How can loss aversion affect portfolio performance?
Loss aversion can have a significant impact on portfolio performance. It can lead investors to hold onto losing investments for longer periods, in the hope that they will eventually recover. This can result in missed opportunities to cut losses and reallocate funds to more promising investments. Additionally, loss aversion may also cause investors to mentally assign higher importance to losses than gains, leading to a more conservative and risk-averse investment approach.
However, it is important to strike a balance. By being aware of the influence of loss aversion, investors can make informed decisions that align with their risk tolerance and investment goals. This may involve periodically rebalancing the portfolio, staying informed about market trends, and seeking professional advice when needed.
3. Can loss aversion lead to missed investment opportunities?
Yes, loss aversion can lead to missed investment opportunities. As mentioned earlier, the fear of experiencing losses can cause investors to shy away from taking risks and exploring potentially lucrative opportunities. This can result in missed chances to capitalize on market upswings and generate higher returns.
To mitigate the impact of loss aversion on missed opportunities, investors can consider diversifying their portfolio with a mix of assets that align with their risk tolerance. It is also important to conduct thorough research and stay informed about emerging trends and market conditions. Finally, seeking advice from financial professionals can help identify investment opportunities that may be missed due to loss aversion bias.
4. Is there a way to manage loss aversion when investing?
While loss aversion is a natural psychological bias, there are strategies that can help manage its impact when investing. One such strategy is to set clear investment goals and develop a well-defined investment plan. This provides a structured approach and helps investors stay focused on their long-term objectives rather than short-term losses.
Another effective approach is to practice regular portfolio reviews and rebalancing. This allows investors to reassess their investments and make necessary adjustments based on changing market conditions. Additionally, seeking advice from financial advisors who can provide an objective perspective can help manage loss aversion and ensure a more rational investment strategy.
5. Can loss aversion ever be beneficial in investment strategy?
While loss aversion tends to be associated with negative outcomes, there can be instances where it can be beneficial in investment strategy. Loss aversion can encourage more cautious decision-making and prompt investors to thoroughly assess the risks and potential downsides before making investment choices. It can act as a protective mechanism, ensuring a more conservative approach during uncertain market conditions.
However, it is crucial to strike a balance and not let loss aversion hinder long-term growth and potential returns. By combining loss aversion with a diversified portfolio, thorough research, and a long-term investment perspective, investors can derive the benefits of cautious decision-making while still capitalizing on investment opportunities.
Loss aversion bias in investing | How biases affect decision-making | Investing Biases | Scripbox
Summary
When it comes to investing, people tend to dislike losses more than they enjoy gains. This psychological bias is called “loss aversion.” It can influence our investment decisions and lead to strategies that may not always be in our best interest.
Loss aversion causes investors to take on less risk and hold onto losing investments longer in hopes of avoiding losses. This can limit potential gains and hinder portfolio growth. To overcome this bias, it’s important to have a balanced investment strategy that considers both the potential for gains and the risk of losses. Diversification and a long-term perspective can help mitigate the negative impact of loss aversion and lead to more successful investment outcomes.





